Hot Streets, Historic Bias: Impacts on Walking in Older U.S. Adults
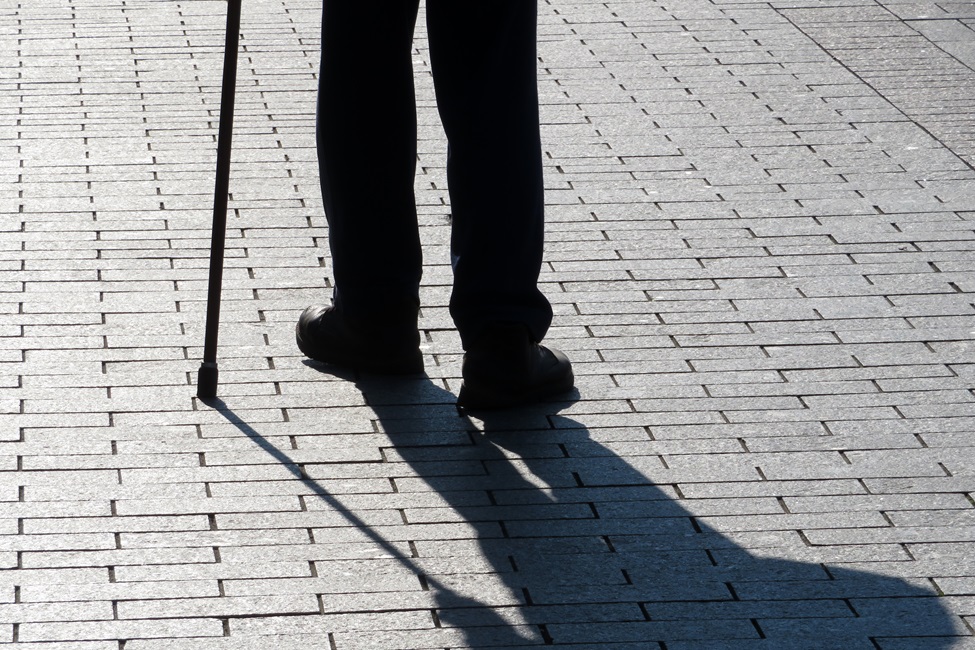

A neighborhood’s walkability is affected by many factors such as street connectivity and density; access to destinations and aesthetics; investment in walking and biking infrastructure; and the presence or absence of urban natural features, specifically tree cover.
Not all neighborhoods are alike. Many neighborhoods in impoverished and minority communities lack the cooling effect of vegetation and tree cover, especially in urbanized areas. As a result, residents face the “heat island effect,” where temperatures remain higher in urban areas compared to the surrounding rural or natural environments.
Past discriminatory housing policies, like redlining, have played a significant role in disproportionately exposing low-income urban communities to extreme heat. Redlining, a practice that began in the United States during the 1930s, involved marking minority, low-income and migrant neighborhoods as “hazardous” with a red color on maps used by the Home Owners' Loan Corporation for mortgage and insurance decisions.
One possible consequence of historic redlining policies is their enduring effect on the built environment, which includes less greenspace and tree cover, coupled with increased pavement, which in turn raises the likelihood of experiencing urban heat island effects.
To date, no known studies have examined the relationships between urban heat islands, historic redlining, and neighborhood walking in older adults.
To fill this gap, a study led by Florida Atlantic University in collaboration with the University of Miami, examined how individual and neighborhood characteristics, including historic redlining scores, vary with how hot the ground gets in the summer (maximum summer land surface temperature). Researchers also investigated whether higher summer land surface temperature is linked to reduced walking in older adults, and if this relationship varies based on historic redlining scores; and whether neighborhoods with higher redlining scores experience higher summer land surface temperatures.
The study, published in the Journal of Urban Health, suggests that discriminatory policies such as historic redlining have left indelible marks on neighborhoods across the U.S., leaving communities more vulnerable to detrimental environmental exposures, including extreme heat.
Results show that higher summer temperatures were linked to reduced neighborhood walking time, though this was significant only for neighborhoods rated as “still desirable” and “best.” In neighborhoods rated as “definitely declining” or “hazardous,” there was no significant link between temperature and walking, which could be due to a lack of alternative recreational activities, or the fact that lower-income residents walk more for essential tasks and cost-saving reasons. Additionally, neighborhoods with poorer redlining scores had higher peak summer temperatures.
“Neighborhoods with historic redlining scores of ‘still desirable’ and ‘best’ tend to have more favorable built and social environments for walking, such as higher socioeconomic status, more greenspace, and better pedestrian amenities,” said Diana Mitsova, Ph.D., senior author and chair and professor of the Department of Urban and Regional Planning within FAU’s Charles E. Schmidt College of Science. “However, we found that people in these affluent neighborhoods walked less when temperatures were higher. This might be because older adults in wealthier areas often have alternative transportation options and other ways to exercise, so they may reduce walking in extreme heat.”
Findings also show:
- People living in the South and West had lower peak summer temperatures compared to those in the Northeast and Midwest
- Neighborhoods with higher area deprivation and more African American/Black residents experienced higher summer temperatures
- Neighborhoods rated as “best” for redlining had lower peak summer temperatures than those with other redlining scores
- Hispanic and Asian individuals, as well as those with higher incomes, were less likely to live in areas with high summer temperatures
“While more research is required, our findings highlight the urgent need to address urban heat islands in historically marginalized communities,” said Mitsova. “This is especially critical as older adults in these areas, who are more vulnerable to heat-related health issues, face greater exposure to extreme temperatures and associated health risks.”
For the study, researchers used data from the 2017 National Household Travel Survey, which included information from more than 260,000 people. They combined this with summer temperature data and linked it to social and environmental characteristics, including historic redlining scores. They also assessed the amount of greenspace in each respondent’s neighborhood. The study focused on 3,982 older adults with an average age of 73 years.
Study co-authors are Lilah M. Besser, Ph.D., and Elaine T. Le, Department of Neurology, Comprehensive Center for Brain Health, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine.
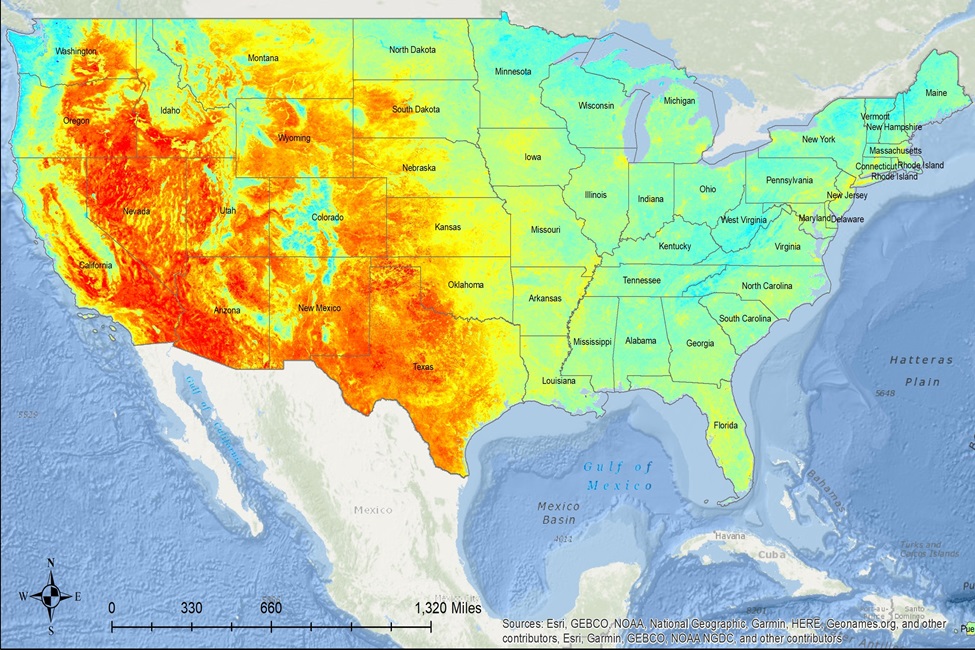
Researchers examined how individual and neighborhood characteristics vary with how hot the ground gets in the summer (maximum summer land surface temperature). Photo credit: Florida Atlantic University (Data Source: National Centers for Environmental Information)
-FAU-
Latest Research
- FAU Named a National Center of Academic Excellence in Cyber ResearchFAU has been recognized as a National Center of Academic Excellence in Cyber Research by the National Security Agency and its partners in the National Centers of Academic Excellence in Cybersecurity.
- FAU Seeks Participants for Parkinson's, Aging and Mind-Body StudyFAU is recruiting participants for an exciting research study aimed at understanding the effects of Parkinson's disease and normal aging on cognitive performance, exercise ability and the mind-body connection.
- Busted! Engineers Revolutionize Fraud Detection with Machine LearningA new breakthrough outperforms traditional methods by generating accurate fraud labels from large, imbalanced datasets, reducing cases needing further inspection, crucial for Medicare and credit card fraud.
- Photobomb: Shark Cam Captures Ocean Encounter With a Great WhiteIn an unprecedented underwater encounter, a nurse shark equipped with a camera tag has captured footage of a great white shark off the coast of Boynton Beach, delighting FAU marine biologists.
- Engineers Bring Sign Language to 'Life' Using AIFAU engineering researchers have developed an innovative interpretation system using AI, which translates American Sign Language gestures into text in real time with 98.2% accuracy.
- Report: Supply Chain Index Declines as Tariffs Hit EconomyThe economy could be headed for a downturn as the supply chain starts to contract amid tariff policies and rising uncertainty, according to researchers at Florida Atlantic University and four other schools.